Flow Cytometry Protocol with Biotinylated Chemokines
Flow cytometry is a powerful technique that can be utilized to measure the interaction of a chemokine with cell surface receptors.
Introduction
Activation of chemokine receptors by their cognate ligands leads to internalization of the receptor-chemokine complexes, which can be monitored by the use of fluorescently labeled ligands. This process can be exploited to detect the receptor expression and has been successfully used to identify the cells expressing the receptors of interest within a complex mixture of primary cells [1,2].
In this protocol, biotinylated CXCL12 (SDF-1a) is pre-mixed with phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated streptavidin and subsequently incubated with U937 cells at 37°C in the presence or absence of AMD3100, a small-molecule inhibitor of its receptor, CXCR4 [3]. CXCL12 internalization is detected by flow cytometry, and its inhibition by AMD3100 suggests the receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Flow cytometry is a powerful technique that can be utilized to measure the interaction of a chemokine with cell surface receptors.
Introduction
Activation of chemokine receptors by their cognate ligands leads to internalization of the receptor-chemokine complexes, which can be monitored by the use of fluorescently labeled ligands. This process can be exploited to detect the receptor expression and has been successfully used to identify the cells expressing the receptors of interest within a complex mixture of primary cells [1,2].
In this protocol, biotinylated CXCL12 (SDF-1a) is pre-mixed with phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated streptavidin and subsequently incubated with U937 cells at 37°C in the presence or absence of AMD3100, a small-molecule inhibitor of its receptor, CXCR4 [3]. CXCL12 internalization is detected by flow cytometry, and its inhibition by AMD3100 suggests the receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Materials
Protocol (avoid prolonged exposure of fluorescent materials to light)
Example Data
- 2 µg CXCL12-biotin [ChemoTactics, B-CXCL12-2ug] reconstituted in 20 µl sterile water (approximately 10 µM)
- Streptavidin-PE [Life Technologies, SA1004-1]
- U937 cells [ATCC, 1593.2]
- RPMI1640 GlutaMax supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum [Life Technologies, 61870-036 and 16000-044]
- Phosphate-buffered saline pH 7.4 [Life Technologies, 10010-023]
- Bovine serum albumin [Sigma, A7906]
- AMD3100 octahydrochloride hydrate [Sigma, A5602]
- Paraformaldehyde [Sigma, 158127]
- Round-bottom 96-well assay plate [Corning, 3788]
Protocol (avoid prolonged exposure of fluorescent materials to light)
- To form the chemokine-streptavidin complex, add 0.4 µl of 10 µM CXCL12-biotin directly to suspension of Streptavidin-PE (consult the manufacturer’s product sheet for the lot-specific concentration) at a molar ratio of 1:4 CXCL12 to streptavidin monomers at room temperature. This represents the amount of CXCL12 required for one reaction. Let the mixture stand for 3 minutes.
- The chemokine-streptavidin complex is mixed with to 200 µl media (RPMI 1640:10% FBS) containing 50,000 U937 cells per well of a 96-well plate. The final CXCL12 concentration is approximately 20 nM.
- As a control for receptor specificity, a parallel reaction may be set up with the simultaneous addition of AMD3100 to a final concentration of 1 µM. If the receptor of interest recognizes more than one chemokine, a competing chemokine can be added at 10X for this purpose. A control for non-specific staining by streptavidin-PE may be required for certain cell types.
- Incubate the reactions for 30 minutes at 37°C.
- After the incubation, briefly chill the assay plate on ice before centrifugation at 400 g for 5 minutes at 4°C. Wash the cells first with 200 µl media two times, and then with 200 µl PBS + 0.5% BSA two times at 4°C.
- Cells may be fixed in 50 µl of 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 5 minutes at room temperature.
- Centrifuge and resuspend the cells in 200 µl PBS + 0.5% BSA and analyze the cellular fluorescence by a flow cytometer.
Example Data
|
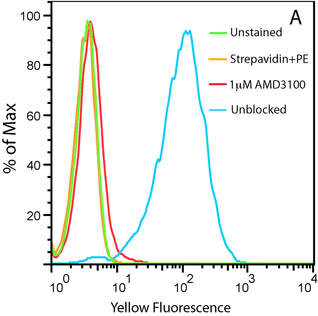
20nM Biotinylated CXCL12 with Streptavidin PE on U937 Cells
Figure A. Uptake of CXCL12-biotin by U937 cells in the presence (red trace) and absence (cyan) of a CXCR4 inhibitor, AMD 3100. U937 cells are not stained by streptavidin-PE in the absence of CXCL12-biotin (orange).
|
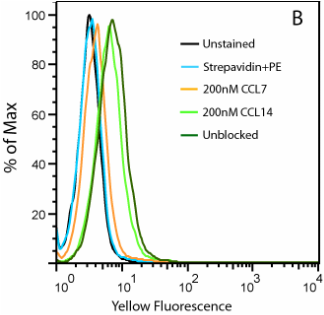
20nM Biotinylated CCL2 with Streptavidin PE on THP-1 Cells
Figure B. Uptake of CCL2-biotin by THP1 cells (dark green trace) is abolished by the addition of CCL7 (orange) but not CCL14 (light green), suggesting a CCR2-specific internalization. THP1 cells are not stained in the absence of CCL2-biotin (cyan).
|
|
Questions about this protocol? Contact us and we can help you.
|
Related Biotinylated Chemokine Products
References
1. McCulloch CV, Morrow V, Milasta S, Comerford I, Milligan G, Graham GJ, Isaacs NW, Nibbs RJ (2008) Multiple roles for the C-terminal tail of the chemokine scavenger D6. J Biol Chem 283:7972–7982.
2. Ford LB, Cerovic V, Milling SW,Graham GJ, Hansell CA and Nibbs RJ (2014) Characterization of Conventional and Atypical Receptors for the Chemokine CCL2 on Mouse Leukocytes. J Immunol 193: 401-11.
3. Fricker SP, Anastassov V, Cox J, Darkes MC, Grujic O, Idzan SR, Labrecque J, Lau G, Mosi RM, Nelson KL, Qin L, Santucci Z, Wong RS. (2006) Characterization of the molecular pharmacology of AMD3100: a specific antagonist of the G-protein coupled chemokine receptor, CXCR4. Biochem Pharmacol 72:588-96.
1. McCulloch CV, Morrow V, Milasta S, Comerford I, Milligan G, Graham GJ, Isaacs NW, Nibbs RJ (2008) Multiple roles for the C-terminal tail of the chemokine scavenger D6. J Biol Chem 283:7972–7982.
2. Ford LB, Cerovic V, Milling SW,Graham GJ, Hansell CA and Nibbs RJ (2014) Characterization of Conventional and Atypical Receptors for the Chemokine CCL2 on Mouse Leukocytes. J Immunol 193: 401-11.
3. Fricker SP, Anastassov V, Cox J, Darkes MC, Grujic O, Idzan SR, Labrecque J, Lau G, Mosi RM, Nelson KL, Qin L, Santucci Z, Wong RS. (2006) Characterization of the molecular pharmacology of AMD3100: a specific antagonist of the G-protein coupled chemokine receptor, CXCR4. Biochem Pharmacol 72:588-96.